Cold Gas
Autonomous and Self-Adaptive High-Resolution 3D Additive Manufacturing Utilizing High-Energy Particle Impacts
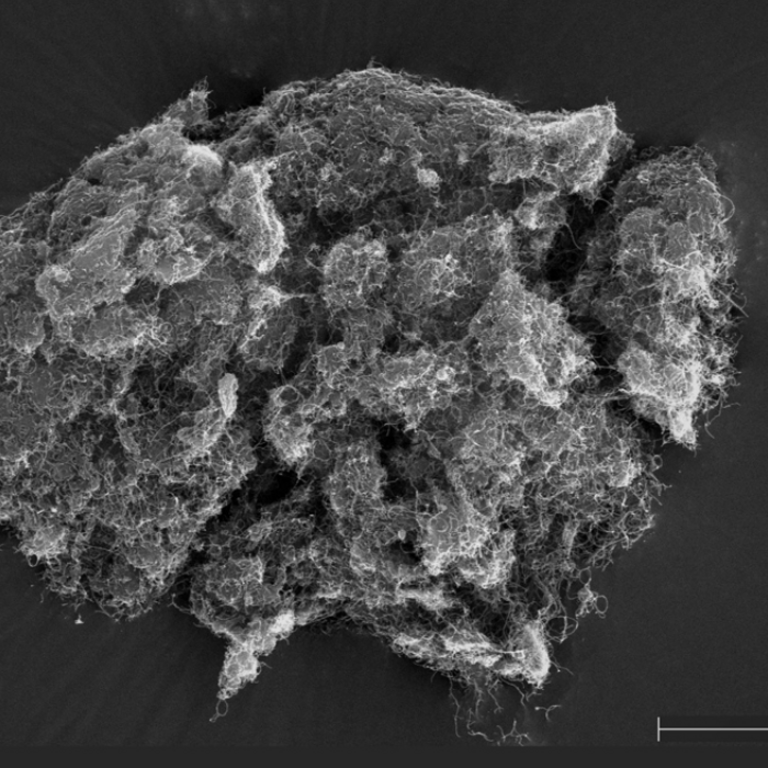
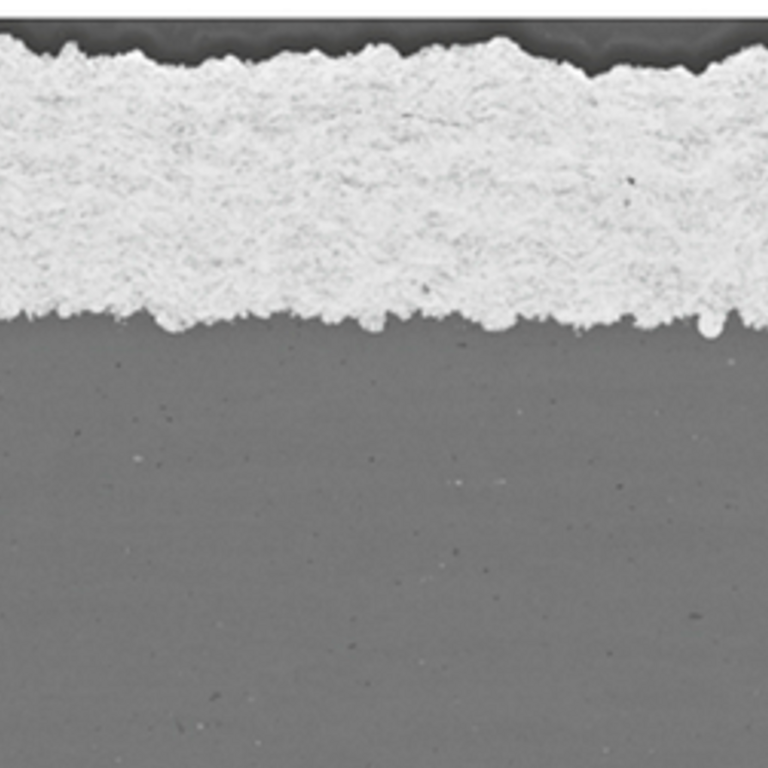
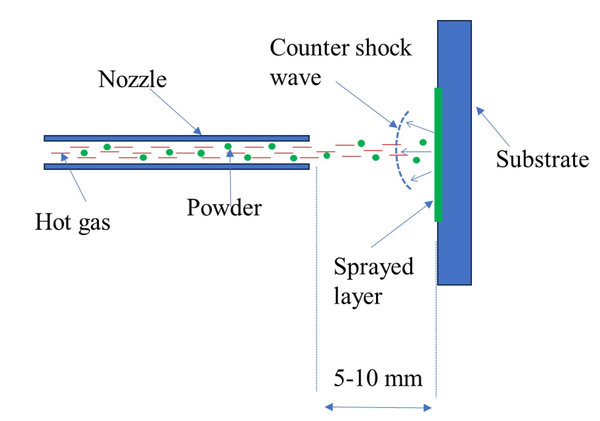
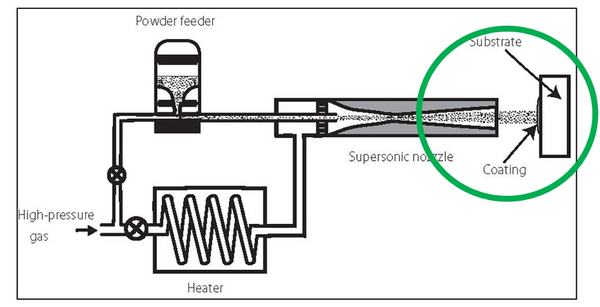
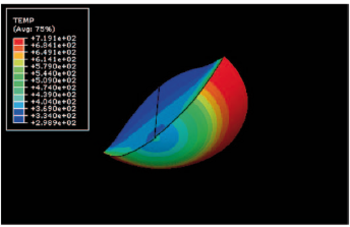
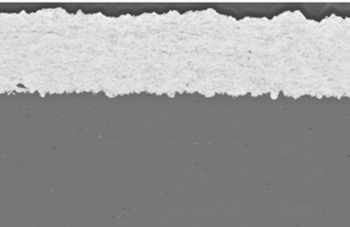
The applicability and efficiency of cold gas-based additive manufacturing processes are significantly influenced by the velocities and temperatures attained by particles upon impact, as these factors are critical for successful deposition onto the material layer being formed. Consequently, they establish the desired operational window for the entire control system. There are two primary challenges in this context.
The first challenge is that the particle velocities and temperatures achieved upon impact are highly dependent on potentially varying raw materials and other unforeseen variations or disturbances within the process chain. The second challenge arises from the fact that the aforementioned desired operational window varies with different raw materials.
To address the first issue, model-based control concepts are currently under investigation. The second challenge is being tackled through the development of a superimposed controller based on real-time optimization, which facilitates adjustments to the desired operational window during standard process operations.
The intended hierarchical control scheme aims to create an autonomous cold gas-spraying-based additive manufacturing process that demonstrates robustness against fluctuations in particle material characteristics (such as size and shape distribution, chemical composition, and thermal conductivity).
DFG Project in the SPP 2364